|
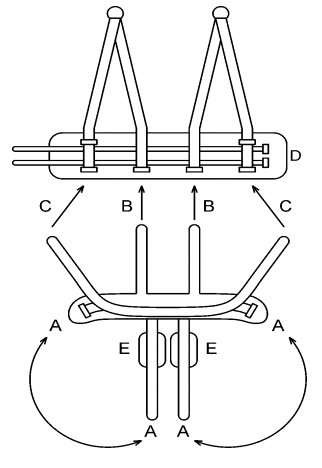
EQUIPMENT FOR LB THERAPY The harness If a patient can already walk on the treadmill without body weight support and is capable of independent walking, the harness is uncritical and any model can be used to serve as (necessary) safety belt. (For safety reasons it is generally not allowed to walk on the Laufband without harness). The only problem then to consider is that the harness does not hinder the patient when walking, e.g. forces him into sitting position or blocks hip extension. With patients who need much body weight support, the
harness and its proper fit are of most critical importance. With
these patients considerable amounts of weight support have to be
applied especially when the patient is not capable of independent
upright standing. Then the harness has to be mounted while the patient
is sitting in the wheel chair. We have developed a harness which
meets these requirements and will be described here in some detail.
A film showing the principles of mounting the harness on differently
disabled patients is included in the CD accompanying the manual
(HARNESS).
Mounting of the harness is described in detail in the included film. |